The Application of Small CNC Milling Machines in the Gold Jewelry Industry
The gold jewelry industry, long revered for its craftsmanship and artistry, has entered a transformative era with the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies. Among these innovations, small Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling machines have emerged as a game-changer, bridging the gap between traditional handcrafting and modern precision engineering. These compact yet powerful tools are redefining how gold jewelry is designed, prototyped, and produced, offering unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and creative freedom.
### **Precision Meets Artistry**
Gold jewelry demands meticulous attention to detail, especially for intricate patterns, filigree work, and personalized engravings. Small CNC milling machines excel in this domain, capable of achieving tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm. This precision ensures consistency across batches—a critical factor for high-end jewelry brands aiming to maintain quality while scaling production. Complex geometries, such as lattice designs or micro-engraved motifs, which once required hours of manual labor, can now be replicated flawlessly using CNC technology.
Moreover, gold’s malleability poses unique challenges during machining. Small CNC mills equipped with high-speed spindles and specialized tooling (e.g., diamond-coated end mills) minimize material deformation, ensuring crisp edges and smooth surfaces. Advanced software further optimizes toolpaths to reduce waste, a significant advantage given the high cost of gold.
### **Accelerating Prototyping and Customization**
In an era where consumers crave bespoke jewelry, small CNC mills empower designers to rapidly iterate prototypes. A 3D model can be transformed into a tangible wax or metal master within hours, streamlining the traditional lost-wax casting process. This agility is particularly valuable for custom engagement rings, pendants, or heirloom pieces, where clients expect quick turnarounds without compromising craftsmanship.
For small-scale workshops or independent jewelers, these machines democratize access to high-end production capabilities. Compact desktop CNC mills, such as Roland’s SRM-20 or Bantam Tools’ models, offer affordability and space efficiency, enabling artisans to experiment with intricate designs previously reserved for large manufacturers.
### **Sustainability and Material Efficiency**
Gold recycling and waste reduction are growing priorities in the jewelry sector. CNC milling’s subtractive manufacturing process generates precise cuts, minimizing excess material. Software simulations further optimize raw material usage, reducing scrap gold by up to 30% compared to manual methods. Additionally, CNC-machined jewelry components often require less post-processing, lowering energy consumption and chemical usage in polishing and finishing stages.
### **Challenges and Adaptations**
Despite their advantages, small CNC mills face hurdles in gold jewelry applications. The softness of pure gold (24K) can lead to tool wear and surface imperfections. To address this, many manufacturers use harder gold alloys (e.g., 18K or 14K) or employ annealing processes to temporarily harden the material before machining. Furthermore, the initial investment in CNC technology and operator training may deter traditional artisans, though hybrid workflows—combining CNC precision with hand-finishing—are gaining traction to preserve artisanal value.
### **Future Trends**
Looking ahead, the integration of AI and machine learning with CNC systems promises to revolutionize jewelry design. AI algorithms could automate toolpath optimization for unprecedented complexity, while additive manufacturing (3D printing) paired with CNC milling might enable hybrid techniques for multi-material jewelry. Additionally, blockchain technology could trace CNC-machined pieces, ensuring ethical sourcing and production transparency—a growing demand among conscious consumers.
### **Conclusion**
Small CNC milling machines are not replacing the jeweler’s artistry but augmenting it. By handling repetitive tasks and enabling hyper-detailed designs, they free craftsmen to focus on innovation and storytelling—the soul of jewelry. As the gold jewelry industry evolves, CNC technology will remain a cornerstone, blending centuries-old traditions with 21st-century engineering to create wearable masterpieces that captivate generations.
 The Application of Small CNC Milling Machines in the Gold Jewelry Industry
The Application of Small CNC Milling Machines in the Gold Jewelry Industry
 Application and Future Trends of Small CNC Milling Machines in Developing Countries: Focus on South America
Application and Future Trends of Small CNC Milling Machines in Developing Countries: Focus on South America
 The Growing Role of Small CNC Milling Machines in Automotive and Motorcycle Parts Manufacturing: A Focus on Emerging Markets
The Growing Role of Small CNC Milling Machines in Automotive and Motorcycle Parts Manufacturing: A Focus on Emerging Markets
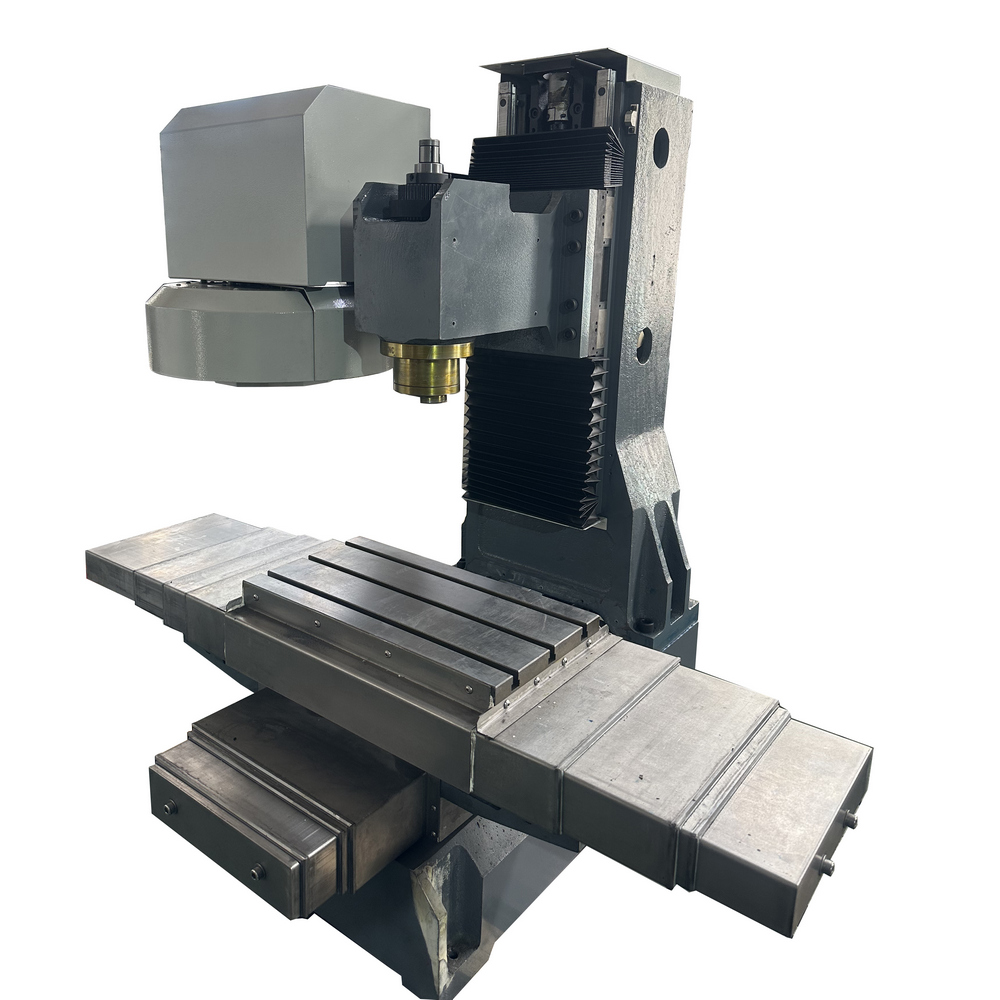 A high-quality CNC small machine starts with a robust frame that is sturdy, stable, and highly precise
A high-quality CNC small machine starts with a robust frame that is sturdy, stable, and highly precise
Please contact us with your request
We are ready to answer your questions.
